Battery Cycle Test Rig
Solution for long term test and qualification of Li-Ion batteries
The Challenge
Micropower builds modular Li-Ion battery packs and chargers for a wide range of applications such as automotive, utility vehicles and mobile storage solutions.
They needed a safe, reliable and flexible test solution that could cycle battery packs unattended for many months, while logging large amounts of measurement data from the DUT (device under test).
The Solution
WireFlow built a test system based on NI’s cRIO-9035 controller, fitted with CAN modules, I/O modules and WireFlow’s WF 3169 C-series module, specifically designed for battery cell measurements.
To handle the large data amounts, the log files are periodically uploaded to a remote NAS (network attached storage) where operators could download data from ongoing tests for analysis.
In addition to log data, the cRIO also controls a 130A battery charger and 3kW programmable load. Li-ion batteries are sensitive so certain protection mechanisms are built in that automatically shut down the test program and physically disconnect the load, charger and batteries from each other.
Operators receive daily email reports of system status and progress as well as notifications if any fault occurs. Live monitoring and control of the system status is done remotely from a desktop PC application.
The whole system is mounted in a 19” rack that can be locked to prevent unauthorized access during tests.
Flexible Cycle Control
The core task of the test system is to alternate between charging and discharging the DUT within pre-set SOC (state of charge) levels. Micropower needed a flexible solution that could be used for multiple batteries and test types; therefore, the operator has the option to define cycles and sub-cycles with individually configurable SOC levels.
The system also provides the option of pausing/resuming an ongoing test in case the equipment needs adjustments.
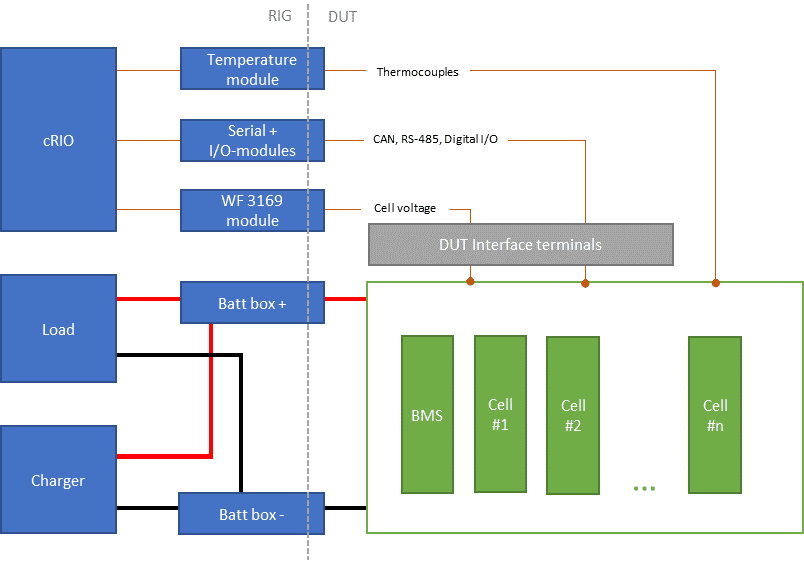
Figure 2 – System Overview
Safety Features for Li-Ion Batteries
Li-ion batteries must never be charged or discharged outside certain voltage bounds, otherwise they can get damaged or catch fire. Battery packs normally have a built-in BMS (battery monitoring system) that monitors the voltage and temperature of the cells. This information is used to control the charge/discharge process and also as a safety mechanism for disconnecting the battery pack.
The test system built by WireFlow has an extra safety layer where the cell voltages, temperatures and a smoke detector are measured and monitored externally by the cRIO. Even if the BMS fails, the system will disconnect the battery pack. The cabinets also have an emergency stop button that turns of the power of the system.
The cRIO-9035 has a built-in FPGA which is ideal for isolating safety features. Therefore, the system uses the FPGA for monitoring the measurement application of the cRIO and disconnects the battery if any software errors occur during measurement.
Remote Control and Monitoring
Cycle tests are normally conducted in a lab environment. To monitor the test progress, it is possible to configure email notifications with daily reports, error reports and when a test is completed.
To control the test system and to get a live view of the current state, it is possible to connect to the cycle rig via a desktop application. The application lets the operator:
- Configure and control the test
- Configure and control the system
- Read the state of system variables
- View live data of any variable
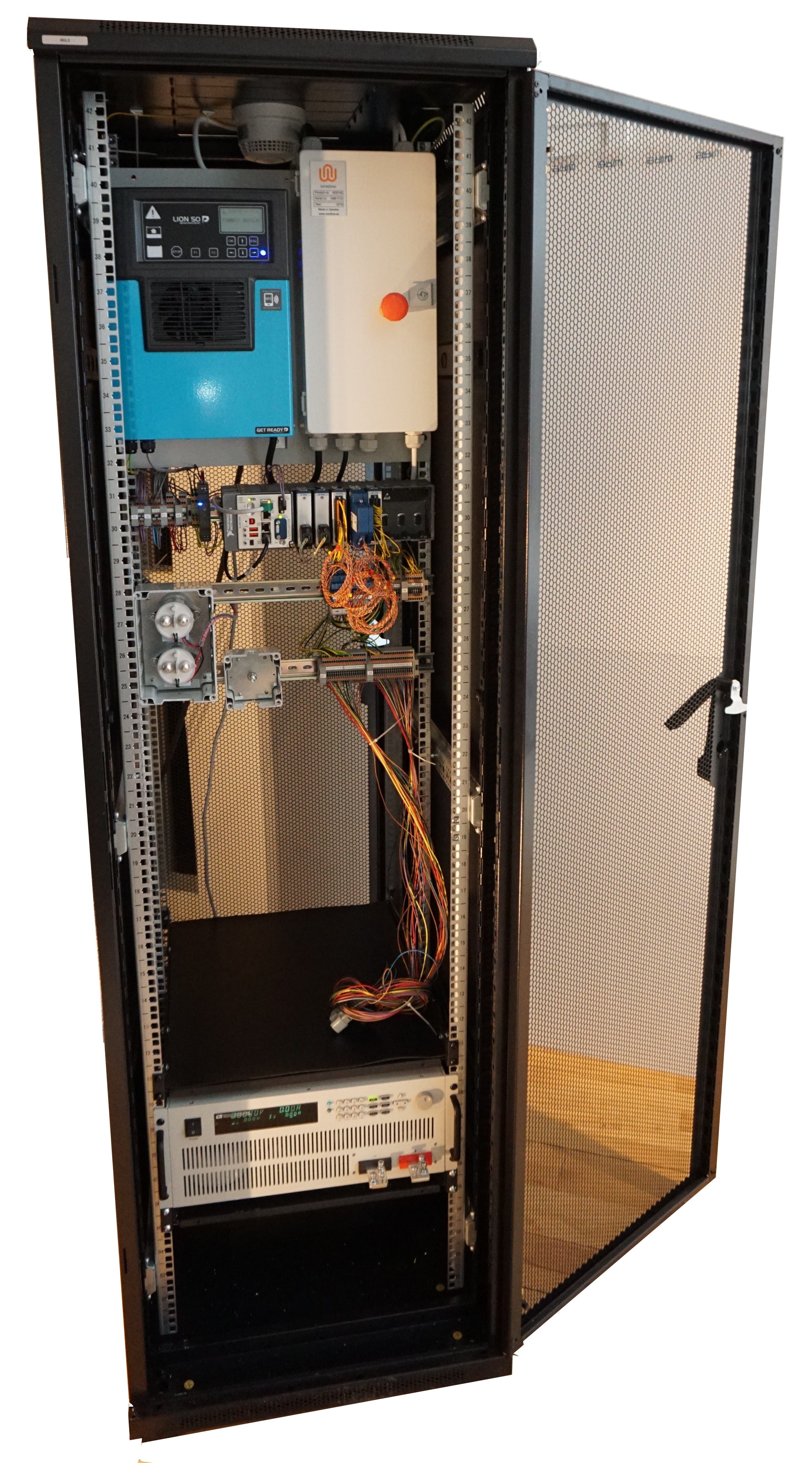

Figure 1 – Cycle Test Rig
Data Logging and Export
The test system logs voltage and temperature of each individual cell of the DUT. In addition to that, it also logs all CAN and RS-485 traffic on the DUT’s internal and external buses.
Several months of logging generates terabytes of data. This data is exported to a remote NAS to protect for integrity and because of space limitations on the cRIO. It also provides a safe barrier for operators that want to analyze the data – accessing it from a NAS instead of the cRIO reduces the risk of accidently interfering with the ongoing measurement.
To protect against network failure between the cRIO and NAS, there is an extra SD-card storage on the cRIO that acts as a buffer until the network is live again.
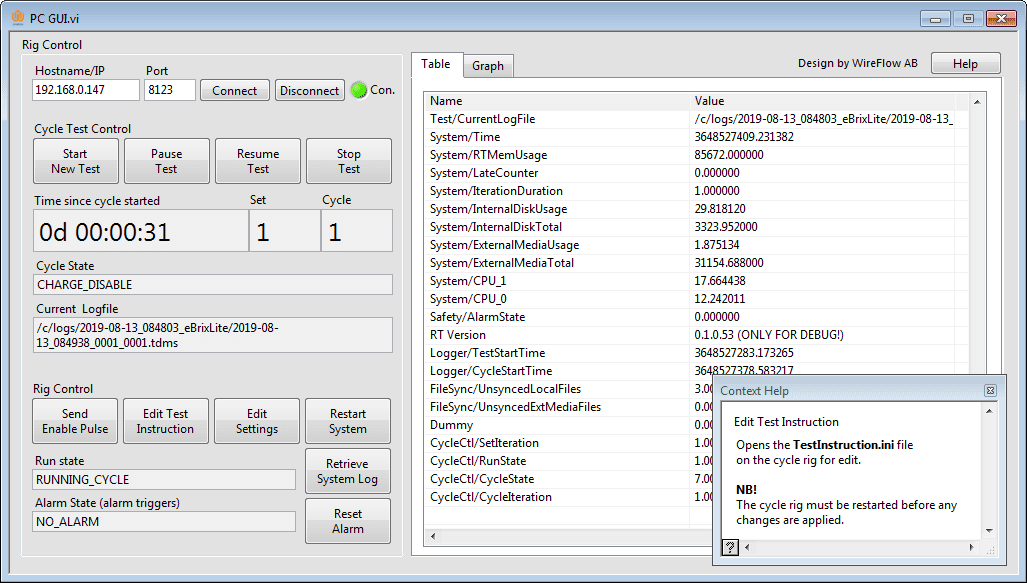
Figure 3 – Desktop PC GUI

